注意注意注意: 异或运算符优先级比等于还要低!!!!二进制的运算符尽量都加上括号
必胜状态后继节点一定有必败
必败状态后继都是必胜
巴什博弈
数上博弈俩人轮流取数,一次可以取走1到m个数,假如有m+1个数,则第一个人怎么取第二个人都可以一次取走, 第二个人就赢了,现在有x个数,这x个数可能是m+1的倍数,也可能不是,假设不是,那么那么第一个人 就可以第一次取s个数,把m+1这个必败状态给对方,假如是,则自己就是必败了 x=n*(m+1)+s
Brave game (HDU1846) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ; int main () { int t; cin >>t; while (t--){ int a,b; cin >>a>>b; int mod=a%(b+1 ); if (mod>=1 ) cout <<"first" <<'\n' ; else cout <<"second" <<'\n' ; } return 0 ; }
Public Sale (HDU2149) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ; int main () { int a,b; while (cin >>b>>a){ int mod=b%(a+1 ); if (a>=b){ for (int i=b;i<=a;i++){ if (i!=a) cout <<i<<' ' ; else cout <<i<<'\n' ; } continue ; } if (mod>=1 ) cout <<mod<<'\n' ; else cout <<"none" <<'\n' ; } return 0 ; }
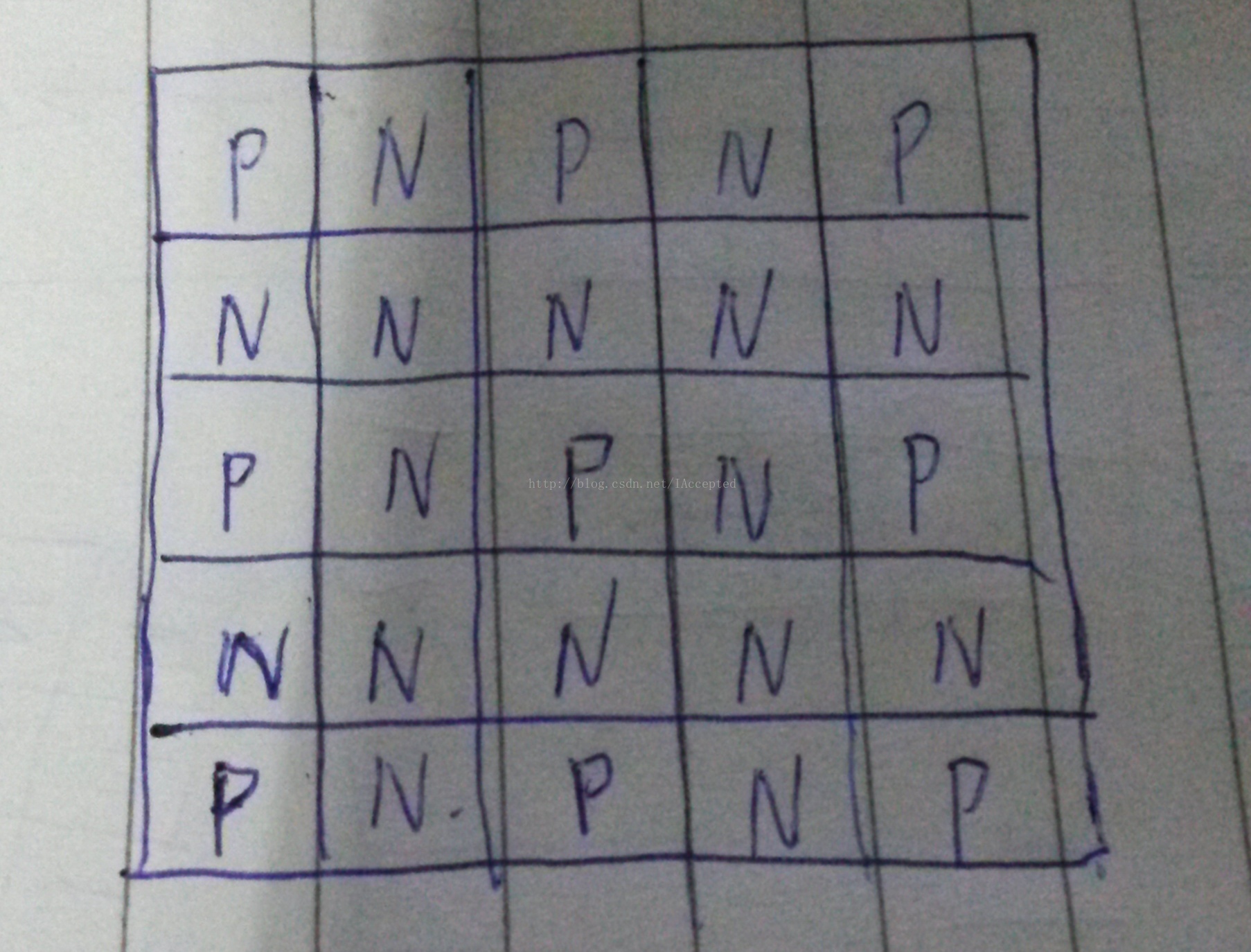
图上巴什博弈问题,终结点为必败点,由终结点去推其他店直到推出起点的属性,最后找规律
只能走到必胜点的是必败点 可以走到必败点的是必胜点
注意: 这里的必败必胜表示的是从这个点开始走的属性而不是走到这个点的属性
kiki’s game (HDU2147)
这道题只要n或者m有一个偶数则起点就是必胜点
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ; int main () { int n,m; while (cin >>n>>m){ if (n==0 && m==0 ) break ; if (!(n&1 ) || !(m&1 )) cout <<"Wonderful!" <<'\n' ; else cout <<"What a pity!" <<'\n' ; } return 0 ; }
斐波那契博弈 当n是一个斐波那契数的时候必胜或者必输,所以对于一道题可以从小推个十来个数,看看必胜或者必输的点如果正好符合斐波那契数列则可以尝试用这种方法
取石子游戏 (HDU2516) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ; typedef long long ll;int fbi[51 ];int main () { fbi[1 ]=2 ; fbi[2 ]=3 ; for (int i=3 ;i<=44 ;i++) fbi[i]=fbi[i-1 ]+fbi[i-2 ]; int n; while (cin >>n){ if (n==0 ) break ; int x=lower_bound(fbi+1 ,fbi+1 +44 ,n)-fbi; if (fbi[x]==n) cout <<"Second win" <<'\n' ; else cout <<"First win" <<'\n' ; } return 0 ; }
威佐夫博弈 这个博弈的证明是非常非常复杂的,而且没啥用,所以只需要记住结论会判断哪一个状态是奇异状态,也就是必败状态就可以了
结论:(判断一个状态是否为奇异状态)
满足上面等式则该状态是奇异状态
取石子游戏 两堆石子,每次可以从两堆石子取走相等数量的石子,或者从一堆中取走任意数量的石子,谁最后没有石子取谁就输了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ; bool check (int a,int b) { int x=(b-a)*(sqrt (5 )+1 )/2 ; if (x==a) return 1 ; return 0 ; } int main () { int a,b; while (cin >>a>>b){ if (a>b) swap(a,b); if (check(a,b)) cout <<0 <<'\n' ; else cout <<1 <<'\n' ; } return 0 ; }
Nim游戏 Being a Good Boy in Spring Festival(HDU1850) 有n堆扑克牌,每堆扑克牌数量为ai,两个人轮流取,每个人可以取走一堆中任意数量的扑克牌,最后没人有牌取就输了
典型nim游戏,奇异局势为当前剩下的所有扑克牌每一堆的数量的异或等于0,即
计算第一步有多少中方式转化为奇异局势,就是用异或和去和a数组中每一个数一一进行异或,就相当于减去了这个数,然后判断得数是否小于a[i],当小于a[i]则表示可以把a[i]通过异或转变成为除了这个数以外其他数的异或和,就变成了奇异局势
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ; int a[1000100 ];int main () { int n; while (cin >>n){ if (n==0 ) break ; int nim=0 ; for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++){ cin >>a[i]; nim^=a[i]; } if (nim==0 ){ puts ("0" ); continue ; } int cnt=0 ; for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++){ int k=nim^a[i]; if (k<a[i]) cnt++; } cout <<cnt<<'\n' ; } return 0 ; }
SG函数 参考文章
所谓SG函数其实本质上就是打表,算出每一个点是否为必败情况
首先定义mex(minimal excludant)运算,这是施加于一个集合的运算,表示最小的不属于这个集合的非负整数。例如mex{0,1,2,4}=3、mex{2,3,5}=0、mex{}=0。
对于任意状态 x , 定义 SG(x) = mex(S),其中 S 是 x 后继状态的SG函数值的集合。如 x 有三个后继状态分别为 SG(a),SG(b),SG(c),那么SG(x) = mex{SG(a),SG(b),SG(c)}。 这样 集合S 的终态必然是空集,所以SG函数的终态为 SG(x) = 0,当且仅当 x 为必败点P时。
【实例】取石子问题
有1堆n个的石子,每次只能取{ 1, 3, 4 }个石子,先取完石子者胜利,那么各个数的SG值为多少?
SG[0]=0,f[]={1,3,4},
x=1 时,可以取走1 - f{1}个石子,剩余{0}个,所以 SG[1] = mex{ SG[0] }= mex{0} = 1;
x=2 时,可以取走2 - f{1}个石子,剩余{1}个,所以 SG[2] = mex{ SG[1] }= mex{1} = 0;
x=3 时,可以取走3 - f{1,3}个石子,剩余{2,0}个,所以 SG[3] = mex{SG[2],SG[0]} = mex{0,0} =1;
x=4 时,可以取走4- f{1,3,4}个石子,剩余{3,1,0}个,所以 SG[4] = mex{SG[3],SG[1],SG[0]} = mex{1,1,0} = 2;
x=5 时,可以取走5 - f{1,3,4}个石子,剩余{4,2,1}个,所以SG[5] = mex{SG[4],SG[2],SG[1]} =mex{2,0,1} = 3;
以此类推…..
x 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8….
SG[x] 0 1 0 1 2 3 2 0 1….
由上述实例我们就可以得到SG函数值求解步骤,那么计算1~n的SG函数值步骤如下:
1、使用 数组f 将 可改变当前状态 的方式记录下来。
2、然后我们使用 另一个数组 将当前状态x 的后继状态标记。
3、最后模拟mex运算,也就是我们在标记值中 搜索 未被标记值 的最小值,将其赋值给SG(x)。
4、我们不断的重复 2 - 3 的步骤,就完成了 计算1~n 的函数值。
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 int f[N],SG[MAXN],S[MAXN];void getSG (int n) { int i,j; memset (SG,0 ,sizeof (SG)); for (i = 1 ; i <= n; i++){ memset (S,0 ,sizeof (S)); for (j = 1 ; f[j] <= i && j <= N; j++) S[SG[i-f[j]]] = 1 ; for (j = 0 ;; j++) if (!S[j]){ SG[i] = j; break ; } } }
一道题如果会打SG表这道题就做出来了,但是就是打不出来😭,就算空间不够,不能纯打SG表也可以根据SG表求规律的,给你那么多的数据总不会求不出来巴
再看一道经典例题:Nim or not Nim?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ; #define MAXN 1000 + 10 int sg (int x) { if (x%4 ==0 ) return x-1 ; if (x%4 ==3 ) return x+1 ; return x; } int main () { ios::sync_with_stdio(0 ); cin .tie(0 ); cout .tie(0 ); int t; cin >>t; while (t--){ int n; cin >>n; int c=0 ; for (int i=1 ;i<=n;i++){ int tmp; cin >>tmp; c^=sg(tmp); } if (c==0 ) cout <<"Bob" <<'\n' ; else cout <<"Alice" <<'\n' ; } return 0 ; }